Our Solution
Malta has developed a long-duration energy storage solution that leverages steam-based heat pump technology to provide a cost-efficient, flexible, and integration-ready option for utility and industrial clients. Known as the Steam Energy Management and Storage (SEMS) system, this groundbreaking technology seamlessly integrates with existing energy infrastructure or operates as a standalone solution, delivering clean, reliable power and heat at scale.
Designed to accelerate decarbonization, Malta SEMS offers grid-scale, synchronous, long-duration storage with unmatched adaptability. Its ability to supply both power and heat makes it the lowest-cost alternative for a single plant, enabling asset owners to adapt to unpredictable market changes over the next decade. By mitigating economic risks, Malta SEMS ensures enduring value that surpasses single-function tools limited to either power or heat, which risk becoming stranded as markets evolve.
Uniquely positioned to support, enhance, and replace the capabilities traditionally provided by fossil fuels, Malta SEMS delivers flexible, scalable solutions essential for advancing the clean energy transition.
How does Malta SEMS work?
Malta's electro-thermal energy storage system is built upon well-established principles in thermodynamics.
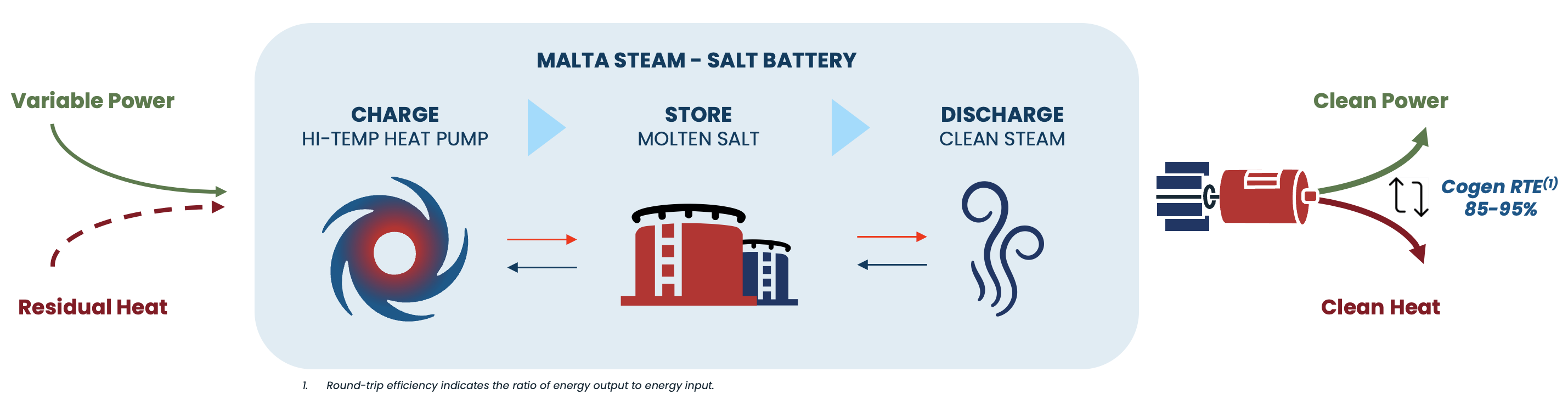
- Renewable energy or energy from the grid charges the system
- Integration with systems that produce excess heat and steam to drive the evaporation process and improve efficiency
- Heat pump (COP > 1.6) with multiple compression stages with intercooling, connected in series produces superheated steam to heat molten salt to 565°C
- The heat is stored in molten salt, and the cold is stored in water (from 8h. to multiday)
- Salt transfers heat to water to produce superheated steam
- Superheated steam flows through a steam turbine to produce electricity or is extracted for heat / steam applications (up to 180bar 550°C)
- Adjustable combinations of power, steam and heat are supplied across applications
- Flexible generation modules enable the ability to integrate with other power / heat / steam generation assets
Materials Used in Malta Steam Energy Management and Storage (SEMS)
Malta's electro-thermal energy storage system is built with abundant, field-proven components that are fully recyclable and reclaimable.
Molten Salt
Molten salt is the most mature technology used in thermal storage. The nitrate salts used by Malta hold heat well and are stable, nonflammable, nonexplosive, and nontoxic, making them a sensible thermal energy storage medium.
Water
Malta SEMS uses water and steam as the working fluid and low temperature storage medium. The choice of steam to run our technology—the most commonly used heat transfer fluid—enables Malta SEMS to integrate seamlessly with the majority of industrial and power generation steam and process cycles worldwide.
Metals, Alloys and Composites
Common metals and alloys, like steel and aluminum, make up the bulk of the piping, turbines, and other mechanical equipment used in a Malta energy storage system.
Cement
Its durability, abundance, and recyclability make it a reliable choice for ensuring long-term system integrity while aligning with sustainable construction practices.